Bowling Ball Core Research Center
Understanding Bowling Ball Cores: The Heart of Performance
The core (also called weight block) is the most important factor in determining how your bowling ball will react on the lane. It affects everything from hook potential to energy retention through the pins.
Why Core Design Matters
Different core shapes create different ball motions. Understanding core types helps you choose equipment that matches your style, rev rate, and the lane conditions you face. The core determines three critical specifications that define ball performance:
Key Core Specifications:
Core Types Explained
There are two main categories of bowling ball cores, each designed for different performance characteristics and bowler types.
Core design affects every aspect of ball performance
Types of Bowling Ball Cores
Choose the right core type to match your playing style and lane conditions
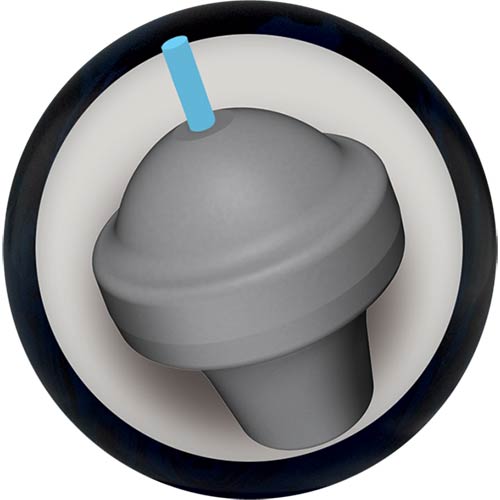
Symmetrical Cores: Predictable Performance
Symmetrical cores have equal weight distribution around the center, creating predictable and controllable ball motion. These cores are ideal for bowlers who want consistent, repeatable reactions.
Symmetrical Core Characteristics:
- Smooth, arcing ball motion – More predictable hook shape
- Less sensitive to ball speed changes – Forgiving for inconsistent releases
- Versatile drilling options – Easier to fine-tune reaction
- Consistent energy transfer – Reliable pin carry
- Excellent for spare shooting – Predictable straight ball motion
Best For:
Beginners learning proper form, league bowlers wanting consistency, players with lower rev rates, and anyone seeking versatile equipment for varying lane conditions.
Popular Symmetrical Core Examples:
R2S cores (Storm), C.A.M. cores (Roto Grip), Centripetal cores (Brunswick), and many more traditional designs.
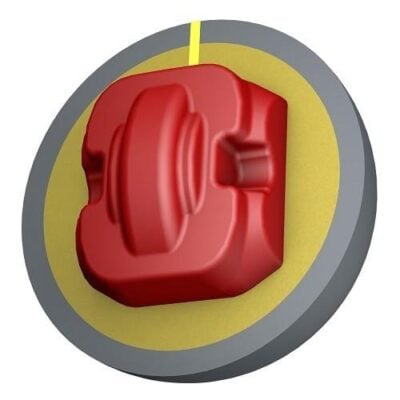
Asymmetrical Cores: Maximum Performance
Asymmetrical cores feature unbalanced weight distribution that creates a mass bias. This imbalance generates stronger, more angular ball reactions and higher hook potential.
Asymmetrical Core Characteristics:
- Stronger backend reaction – More angular entry angle
- Higher hook potential – Maximum track flare capability
- More drilling layout options – Fine-tune ball motion precisely
- Better performance in heavy oil – Cuts through oil patterns
- Increased pin action – Higher strike potential
Best For:
Advanced bowlers with higher rev rates, players facing heavy oil conditions, tournament competitors needing maximum performance, and bowlers wanting aggressive backend reaction.
Popular Asymmetrical Core Examples:
RAD4 cores (Storm), Ikon cores (Roto Grip), DynamiCore technology (Brunswick), and other high-performance designs.
Find Bowling Balls by Core Specifications
Search our complete database by the specific core characteristics that matter to your game
Bowling Ball Core Libraries by Brand
Explore core designs from all major bowling ball manufacturers
How to Choose the Right Core for Your Game
Select the perfect core design based on your skill level, playing style, and typical lane conditions.
For Beginners & Developing Players:
Start with symmetrical cores that offer predictable, controlled reactions. Look for moderate RG values (2.48-2.53) and lower differentials (0.020-0.040) that provide forgiveness while you develop consistency.
For Intermediate Players:
Experiment with both symmetrical and asymmetrical cores. Focus on finding cores that complement your rev rate and speed. Medium differentials (0.030-0.050) offer versatility for different lane conditions.
For Advanced Players:
Consider high-performance asymmetrical cores for maximum versatility. Look for cores with higher differentials (0.045+) and specific RG values that match your technique and the oil patterns you face.
Core Matching Tips:
- Low Rev Rate: Choose cores with lower RG values for earlier rev-up
- High Rev Rate: Higher RG cores give you length and backend reaction
- Dry Lanes: Lower differential cores prevent over-reaction
- Heavy Oil: Higher differential cores cut through oil patterns
- Versatility: Symmetrical cores work on more conditions
Core FAQ – Common Questions
Q: What’s more important – core type or coverstock?
A: Both matter, but core determines the fundamental ball motion while coverstock affects how it reacts to oil. Start with the right core, then fine-tune with surface adjustments.
Q: Can I change my ball’s reaction without buying a new one?
A: Yes! Surface changes (sanding, polishing) and drilling layout adjustments can significantly alter your ball’s performance, but the core’s basic characteristics remain constant.
Q: How many different core types should I have in my arsenal?
A: Most bowlers benefit from 2-4 different core designs: a low-differential symmetrical for spares/dry lanes, a medium-differential option for typical conditions, and higher-performance cores for challenging oil patterns.
Why Bowlers Trust Our Core Research
Comprehensive, accurate, and regularly updated core information
Complete Database
Comprehensive core information from all major manufacturers with detailed specifications and performance data.
Expert Analysis
Professional insights on core performance and applications from certified bowling professionals.
Regular Updates
Latest core designs and specifications added continuously as manufacturers release new products.
Free Resources
Access to core research tools, educational content, and selection guides at no cost.